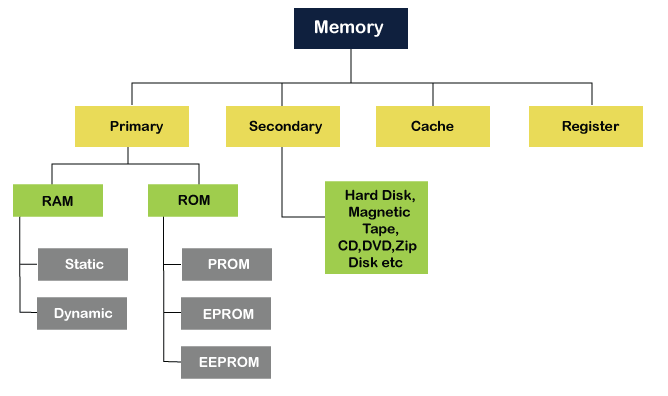
Computer Memory
Computer memory is any physical device, used to store data, information or instruction temporarily or permanently. It is the collection of storage units that stores binary information in the form of bits. The memory block is split into a small number of components, called cells. Each cell has a unique address to store the data in memory, ranging from zero to memory size minus one.
Main memory
Main memory is computer memory that a processor or computer accesses first or directly. It allows a processor to access running execution applications and services that are temporarily stored in a specific memory location. Main memory is also known as primary storage or Primary memory.
The Main memory is further divided into two parts:
- RAM (Random Access Memory)
- ROM (Read Only Memory)
Auxiliary memory
Auxiliary memory is a permanent storage space to hold a large amount of data. It is a storage device that the CPU cannot access directly. It is a permanent storage device. It is also known as Secondary storage/memory. A secondary storage device organizes data into files and directories based on a file system. It also allows the user to access or use additional information like access permissions, owner, last access time, etc. Secondary memory devices are less expensive and can store vast amounts of data, audio, video, and multimedia files. Organizations can store the equivalent of a roomful of data on disks that consume dramatically and significantly less physical space.
Memory hierarchy
The five levels in a memory hierarchy are categorized based on speed and usage. The levels in a memory hierarchy are the following:
Level 0: CPU registers
Level 1: Cache memory
Level 2: Primary memory or main memory
Level 3: Secondary memory or magnetic disks or solid-state storage
Level 4: Tertiary memory or optical disks or magnetic tapes